Abstract
Introduction: Epstein Barr virus-positive (EBV+) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), not otherwise specified (NOS) is a newly recognized entity by the World Health Organization. EBV+ DLBCL, NOS is commonly encountered in Latin American countries and carries a dismal prognosis. Current prognostic models such as the Oyama and the International Prognostic Index (IPI) score have limited prognostic value in this patient population. Therefore, we aim to evaluate the ability of these models to risk stratify patients and propose a novel prognostic model in the largest cohort of Latin American patients with EBV+ DLBCL, NOS.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included patients ≥18 years from six Latin American countries diagnosed and treated at tertiary centers from 2010 to 2020. Hematopathologists at each institution reviewed pathological samples to confirm the diagnosis of EBV+ DLBCL, NOS. We collected clinicopathological data by reviewing the medical records of the patients. The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS), defined as the time from the date of diagnosis until death from any cause or last visit. The secondary endpoint, progression-free survival (PFS), was defined as the time from diagnosis until death, progression, or last visit. Our novel model (Grupo de Estudio Latinomericano de Linfoproliferativos [GELL] Score) includes the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status ≥2, extranodal involvement >1, serum albumin <3.5 g/dL, serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) above the upper limit of normal, and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio >455. We assigned a value of 1 to each of the abovementioned elements in the score and classified the patients as low (0 points), intermediate (1-2 points), and high (3-5) risk. OS and PFS probabilities were computed with the Kaplan-Meier method and compared with the log-rank test. We used Cox regression to evaluate the proportional hazard ratios (HR) of each score for our study outcomes. The C-index was employed to measure discrimination of each model. We used cross-validation to evaluate the model performance.
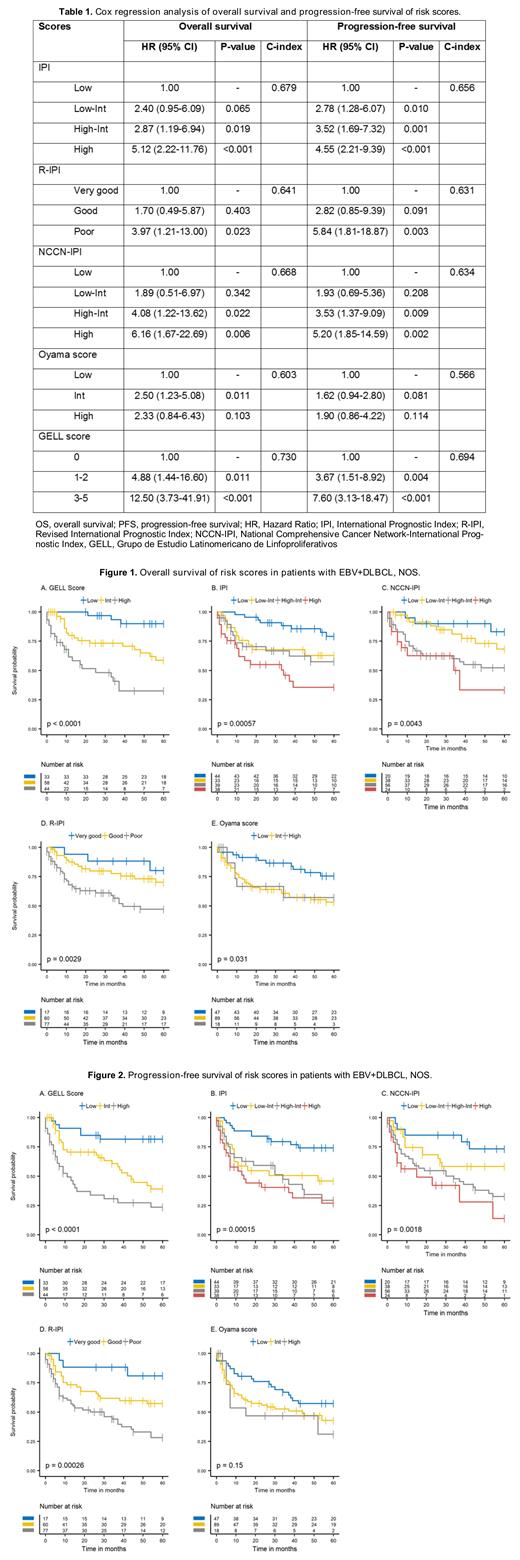
Results: A total of 154 patients with EBV+ DLBCL, NOS were included in this analysis. The median age at diagnosis was 58 years (range 19-86 years) with a slight male predominance (53%). EBER was positive in all cases (range 1-100%). Clinically, 39% presented ECOG ≥2, 57% had B symptoms, 50% had an extranodal disease as a primary tumor, and 71% had Ann Arbor stage III/IV. Fifty-one percent of the patients had an elevated LDH level, and 43% had albumin <3.5 g/dL. Rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) regimen was administered in 79% of individuals as first-line treatment. The overall response rate was 80% (62% complete response and 18% partial response). With a median follow-up of 61 months, the 5-year OS and PFS rates were 61% and 47%, respectively. The 5-year OS rates of patients with low, intermediate, and high-risk disease according to the GELL score was 90%, 59%, and 33%, respectively (Fig 1A). The 5-year PFS rates were 82%, 39%, and 23%, respectively (Fig 2A). Table 1 shows the Cox regression and the discrimination analysis for each of the scores. The GELL score has the highest discriminatory index for OS and PFS compared to the IPI, Revised-IPI, National Comprehensive Cancer Network-IPI, and the Oyama score (Figure 1 and 2).
Conclusions: This study proposes a novel score for risk stratification of patients with EBV+ DLBCL, NOS. The GELL score appears to better discriminate OS and PFS than previous scores. Our results should be validated in an independent prospective cohort.
Ramirez-Ibarguen: Asofarma: Consultancy; MSD: Consultancy; Abbvie: Speakers Bureau; Astra Zeneca: Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Speakers Bureau; Roche: Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Perini: Janssen: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Astra Zeneca: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; MSD: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Oliver: Roche: Other: conference support and fees ; Abbvie: Other: conference support and fees . Castillo: Abbvie: Consultancy, Research Funding; BeiGene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal